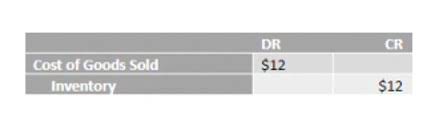
This is consistent with financial reporting where current assets and liabilities are always reported before long-term assets and liabilities. Although the balance sheet always balances out, the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing. If a business buys raw materials and pays in cash, it will result in an increase in the company’s inventory (an asset) while reducing cash capital (another asset). Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting.

Accounting Equation Explained – Definition & Examples
Double-entry accounting is a system where every transaction affects at least two accounts. Notice that every transaction results in an equal effect to assets and liabilities plus capital. An owner registers their new company with the state department of business licensing. They take their business license down to the bank and transfer $20,000 of their own money into a new business account. They have now “capitalized” their business, which means they made a contribution to capital, which increases owner’s equity.

Arrangement #3: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Capital – Owner’s Drawings + Revenues – Expenses
- CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
- If the equation is balanced then the financial statement can be prepared.
- The accounting equation represents a fundamental principle of accounting that states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and equity.
- A debit refers to an increase in an asset or a decrease in a liability or shareholders’ equity.
- Understanding how to use this formula and other necessary basic accounting terms is crucial for finance professionals as it helps to verify the accuracy of records.
Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity represent how the assets of a company are financed. If it’s financed through debt, it’ll show as a liability, but if it’s financed through issuing equity shares to investors, it’ll show in shareholders’ equity. You can automatically generate and send invoices using this accounting software. Further, creating financial statements has become considerably easier thanks to the software, which lets you draft balance sheets, income statements, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements. Before technological advances came along for these growing businesses, bookkeepers were forced to manually manage their accounting (when single-entry accounting was the norm). Of course, this lead to the chance of human error, which is detrimental to a company’s health, balance sheets, and investor ability.

What is Accrual Accounting and How it Works: Basics & Examples
In the accounting equation, every transaction will have a debit and credit entry, and the total debits (left side) will equal the total credits (right side). For a company keeping accurate accounts, every business transaction will be represented in at least two of its accounts. For instance, if a business takes a loan from a bank, the borrowed money will be reflected in its balance sheet as both an increase in the company’s assets and an increase in its loan liability. The accounting equation helps to assess whether the business transactions carried out by the company are being accurately reflected in its books and accounts. It’s telling us that creditors have priority over owners, in terms of satisfying their demands. While the basic accounting equation’s main goal is to show the financial position of the business.
Understanding the Core Components of the Accounting Equation
- Any increase in these increases the financial commitment of a company and reduces equity if not managed well.
- Before getting into how the accounting equation helps balance double-entry bookkeeping, let’s explain each element of the equation in detail.
- The assets that an owner contributes to a business are known as investments.
- Using the two forms of the accounting equation, insert these figures into each equation to show that the equation holds true in both cases.
Time value of money (TVM) refers to the concept that money available today is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its earning potential. However, the accounting equation treats all values at face value regardless of when they are realized. This becomes problematic when dealing with long-term assets or liabilities. The inventory (asset) of the business will increase by the $2,500 cost of unearned revenue the inventory and a trade payable (liability) will be recorded to represent the amount now owed to the supplier. An asset is a resource that can provide current or future economic benefit to the organization who owns or controls the asset.
What is Qualified Business Income?
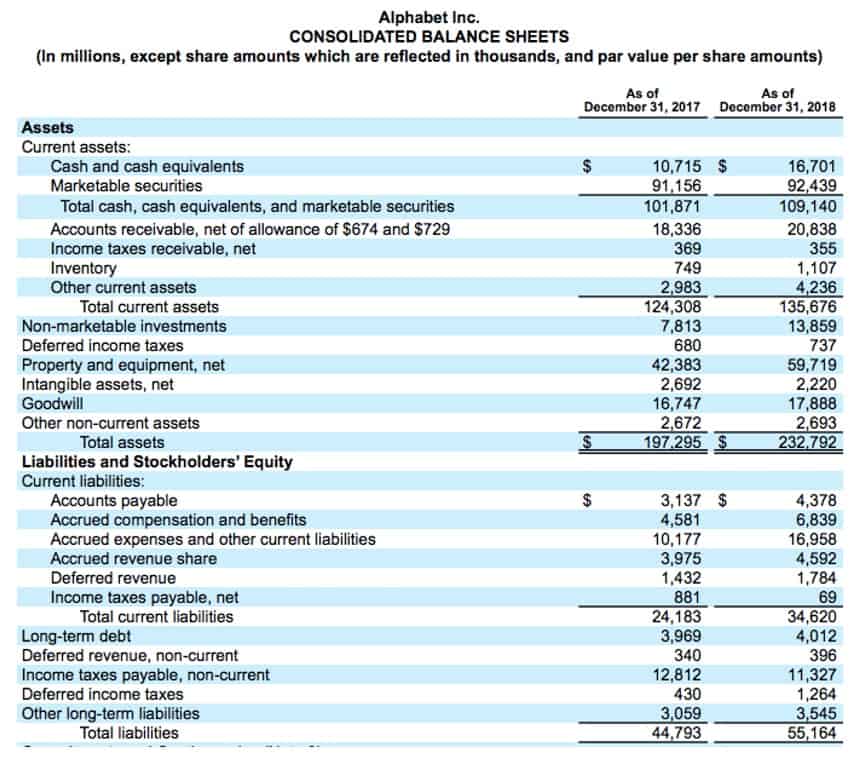
Assets are reported on a company’s balance sheet and comprises various asset types such as intangible assets, financial assets, fixed assets and current assets. The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance. Ted is an entrepreneur who wants to start a company selling speakers for car stereo systems. After saving up money for a year, Ted decides it is time to officially start his business. He forms Speakers, Inc. and contributes $100,000 to the company in exchange for all of its newly issued shares. This business transaction increases company cash and increases equity by the same amount.
- On the balance sheet, the accounting equation gives a clear view of financial health by showing how much the company owes and what it owns.
- One quality that is shared by all assets is the ability to continue providing services or benefits into the foreseeable future.
- The purpose of the accounting equation is that it lays the framework for the accounting processes and ensures integrity in financial transaction recording.
- Although the balance sheet always balances out, the accounting equation can’t tell investors how well a company is performing.
- At first glance, you probably don’t see a big difference from the basic accounting equation.
- The accounting equation doesn’t consider these currency transactions, which gives a false view of a company’s financial position if it is operating globally.
This simple formula can also be expressed in three other ways, which we’ll cover next. At first glance, this may look overwhelming — but don’t worry because all three reveal the same information; it just depends on what kind of information you’re looking for. For example, the use of raw materials and packaging materials are both considered to be part of internal transactions. These activities are typically carried out with the purpose of earning money.
The assets of the business will increase by $12,000 as a result the accounting equation can be expressed as of acquiring the van (asset) but will also decrease by an equal amount due to the payment of cash (asset). Required Explain how each of the above transactions impact the accounting equation and illustrate the cumulative effect that they have. We will now consider an example with various transactions within a business to see how each has a dual aspect and to demonstrate the cumulative effect on the accounting equation. In the case of a limited liability company, capital would be referred to as ‘Equity’. If a transaction is completely omitted from the accounting books, it will not unbalance the accounting equation. This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1.